Despite their unique similarities, eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells have distinct disparities. Eukaryotic cells are those cells that have a membrane-bound organelles, which is inclusive of the nucleus. Eukaryotes can be single-celled and they can also be multi-celled organisms such as plants, mammals and insects among others. Additionally, it is the nucleus of the eukaryotic cells that give the eukaryotes their name. Also, this is because the term eukaryote denotes true nucleus. Contrary, prokaryotes are unicellular organisms, which do not have a nucleus that is membrane bound. Prokaryotes also lack membrane-bound mitochondria and all its other organelles do not have a membrane protective shield.
Comparison and Contrast of Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes
Similarities
There are no many similarities between eukaryotes and prokaryotes. However, both types of cells contain a plasma membrane which is also known as a cell membrane (Kumar, 2013). The plasma membrane is the biological membrane, which separates the interior of a cell from the external environment of the cell, which is also known as the extracellular space. Also, both eukaryotes and prokaryotes has a cytoplasm, which is the matter within the living cells with the exclusion of the nucleus.
Differences
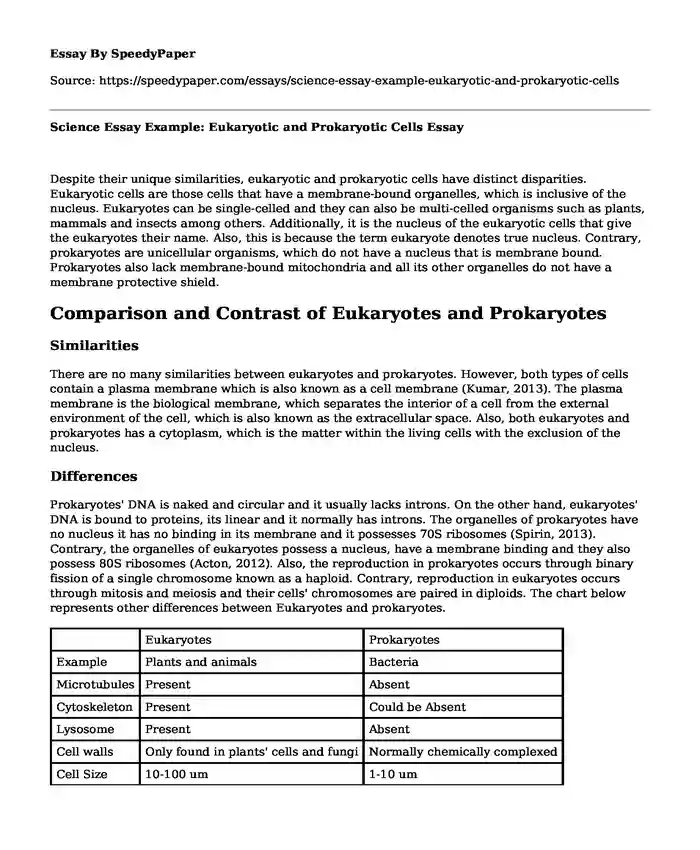
Prokaryotes' DNA is naked and circular and it usually lacks introns. On the other hand, eukaryotes' DNA is bound to proteins, its linear and it normally has introns. The organelles of prokaryotes have no nucleus it has no binding in its membrane and it possesses 70S ribosomes (Spirin, 2013). Contrary, the organelles of eukaryotes possess a nucleus, have a membrane binding and they also possess 80S ribosomes (Acton, 2012). Also, the reproduction in prokaryotes occurs through binary fission of a single chromosome known as a haploid. Contrary, reproduction in eukaryotes occurs through mitosis and meiosis and their cells' chromosomes are paired in diploids. The chart below represents other differences between Eukaryotes and prokaryotes.
| Eukaryotes | Prokaryotes | |
| Example | Plants and animals | Bacteria |
| Microtubules | Present | Absent |
| Cytoskeleton | Present | Could be Absent |
| Lysosome | Present | Absent |
| Cell walls | Only found in plants' cells and fungi | Normally chemically complexed |
| Cell Size | 10-100 um | 1-10 um |
| Ribosomes | Bigger | Smaller |
Examples of Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes
Almost all living things that can be observed without the need of a microscope are considered to be eukaryotes. Examples of such organisms include animals, fungi and plants. Contrary, prokaryotic living organisms contain a single cell and unlike eukaryotes, their cells are very small. One example of prokaryotic living organism is a bacterium like E. coli.
Significance of the Difference Between the Two Kinds of Cells
The knowledge between the two kinds of cells is important because cells contain hereditary data, which is passed through cell division. As such, they provide essential data about life. Also, since all cells originate from other cells, it is possible to learn about the growth and reproduction of different forms of cells.
Reasons Why Scientists Insist on the Difference
The primary reason why scientists insist on having a distinct knowledge of the two kinds of cells is that the knowledge of the differences enable the scientists to identify the distinguishable characteristics between the cells. Subsequently, with such knowledge, it is possible for the scientists to know how treat, reproduce and eradicate different organisms based on their cell compositions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, despite their unique similarities, eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells have distinct disparities. Additionally, eukaryotic cells have a cell membrane, are single-celled and they can also be multi-celled organisms such as plants, mammals and insects among others. On the other hand, prokaryotes are unicellular organisms, which do not have a nucleus and mitochondria that is membrane bound.
References
Acton, Q. A. (2012). Organelles: Advances in Research and Application: 2011 Edition. Atlanta: ScholarlyEditions.
Kumar, A. (2013). Eukaryotic Gene Expression. Berlin: Springer Science & Business Media.
Spirin, A. (2013). Ribosomes. Berlin: Springer Science & Business Media.
Cite this page
Science Essay Example: Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells. (2022, Jul 08). Retrieved from https://speedypaper.net/essays/science-essay-example-eukaryotic-and-prokaryotic-cells
Request Removal
If you are the original author of this essay and no longer wish to have it published on the SpeedyPaper website, please click below to request its removal:
- Essay Sample on Service Dogs
- Organizational Goals Essay Sample
- Economics Essay Sample: Introduction to the American Economy
- Free Essay Example on Social Classes in Mande
- Essay Example Discussing the Issues in Tech Integration (Privacy)
- History and the Achievements of Women in Mathematics - Essay Example
- Factors Influencing Employee Motivation. Paper Example
Popular categories